1. What are the types of temperature sensors?
A temperature sensor refers to a sensor that can sense temperature and convert it into a usable output signal. Temperature sensors are the core part of temperature measurement instruments and come in many varieties.
(1) According to the measurement method, it can be divided into two categories: contact type and non-contact type.
1. Contact type
The detection part of the contact temperature sensor has good contact with the object being measured, and is also called a thermometer.

The thermometer works by conduction or convection Achieve thermal equilibrium, so that the indication value of the thermometer can directly represent the temperature of the measured object. Generally, the measurement accuracy is higher. Within a certain temperature measurement range, the thermometer can also measure the temperature distribution inside the object. However, large measurement errors will occur for moving objects, small targets or objects with small heat capacity.
Commonly used thermometers include bimetal thermometers, liquid-in-glass thermometers, pressure thermometers, resistance thermometers, thermistors and thermocouples, etc., which are widely used in industry, agriculture, commerce and other sectors.
2. Non-contact type
Its sensitive element does not come into contact with the object being measured, and it is also called a non-contact temperature measurement instrument. This instrument can be used to measure the surface temperature of moving objects, small targets and objects with small heat capacity or rapid temperature changes (transient). It can also be used to measure the temperature distribution of the temperature field.
The most commonly used non-contact temperature measurement instrument is based on the basic law of blackbody radiation and is called a radiation thermometer. Radiation thermometry includes brightness method, radiation method and colorimetric method.
Advantages of non-contact temperature measurement: The upper limit of measurement is not limited by the temperature resistance of the temperature sensing element, so in principle there is no limit to the maximum measurable temperature. For high temperatures above 1800°C, non-contact temperature measurement methods are mainly used. With the development of infrared technology, radiation temperature measurement has gradually expanded from visible light to infrared. It has been used from temperatures below 700°C to room temperature, and the resolution is very high.
(2) According to the characteristics of sensor materials and electronic components, they are divided into two categories: thermal resistors and thermocouples.
1. Thermistor
Thermistor is made of semiconductor materials, most of which have negative temperature coefficients, that is, the resistance increases as the temperature increases. reduce.
Temperature changes will cause large resistance changes, so it is the most sensitive temperature sensor. However, the linearity of the thermistor is extremely poor and has a lot to do with the production process.
Thermistors also have their own measurement techniques. The small size of the thermistor is an advantagepoint, it stabilizes quickly and does not cause thermal load. However, it is also very fragile, and large currents can cause self-heating. Since the thermistor is a resistive device, any current source will cause heat to be generated by power across it. Power is equal to the square of the current times the resistance. Therefore use a small current source. If the thermistor is exposed to high heat, permanent damage will occur.
2. Thermocouple
Thermocouple is the most commonly used temperature sensor in temperature measurement. Its main advantages are wide temperature range and adaptability to various atmospheric environments. It is also sturdy and low-priced. It does not require power supply and is also the cheapest. Thermocouples are the simplest and most versatile temperature sensors, but thermocouples are not suitable for high-precision measurements and applications.
2. Working principles of various temperature sensors
1. Working principles of thermocouple sensors
When there are two different conductors and semiconductors A and B forming a loop, and the two ends are connected to each other, as long as the temperatures at the two nodes are different, the temperature of one end is T, which is called the working end or hot end, and the temperature of the other end is TO , called the free end or cold end, then there will be current in the loop, that is, the electromotive force existing in the loop is called thermal electromotive force. This phenomenon of electromotive force generated due to temperature differences is called the Seebeck effect. There are two effects related to Seebeck: First, when a current flows through the connection of two different conductors, heat is absorbed or released (depending on the direction of the current), which is called the Peltier effect; the other Second, when a current flows through a conductor with a temperature gradient, the conductor absorbs or releases heat (depending on the direction of the current relative to the temperature gradient), which is called the Thomson effect. A combination of two different conductors or semiconductors is called a thermocouple.
2. Working principle of resistance sensor
The resistance value of the conductor changes with the temperature change. By measuring its resistance value, the temperature of the measured object can be calculated. The sensor constructed using this principle is a resistance temperature sensor. This sensor is mainly used for temperature measurement in the temperature range of -200-500°C. Pure metal is the main manufacturing material of thermal resistor. The material of thermal resistor should have the following characteristics:
(1). The temperature coefficient of resistance should be large and stable, and there should be a good linear relationship between resistance value and temperature. .
(2). High resistivity, small heat capacity and fast reaction speed.
(3). The material has good reproducibility and processability, and the price is low.
(4). The chemical and physical properties are stable within the temperature measurement range.
At present, platinum and copper are the most widely used in industry, and have been made into standard temperature measuring thermal resistors.
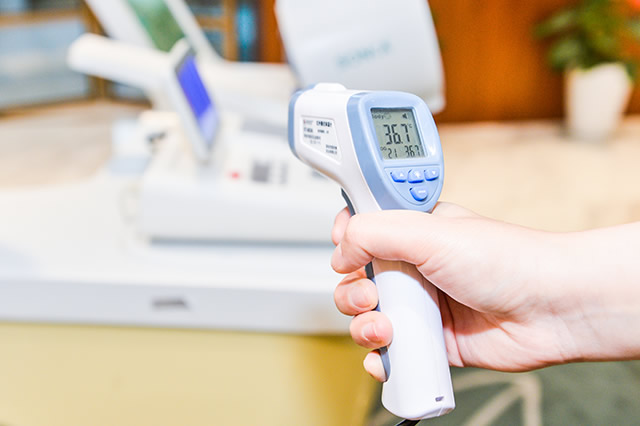
3. Principle of infrared temperature sensor
In nature, when the temperature of an object is higher than absolute zero, due to the existence of internal thermal motion, will continuously radiate electromagnetic waves to the surroundings, whichIt contains infrared rays with a band between 0.75 and 100 μm. Infrared temperature sensors are made using this principle.
If the website content violates your rights, please contact us to delete it。